Commonly Used Terminology
xy-plane and ordered pair
xy-plane refers to a coordinate system that has a horizontal x-axis and a vertical y-axis. See figure below. The y-axis is perpendicular to the x-axis. The point where the two axes meet is known as the origin.
Each point in the coordinate system has a coordinate on the x-axis and a coordinate on the y-axis, collectively known as the ordered pair (x, y). For example, in the figure below, the x-coordinate of point A is 3 and the y-coordinate is 1. The ordered pair is written as (3, 1). The coordinates of origin are (0, 0).
Since every point on a line or a curve graph is plotted on the x- and y-axes, the term is used in questions to logically represent a line or a curve on a graph.

Quadrant
The four sections formed by the intersecting x- and the y-axes in the xy-plane are known as quadrants. See figure above. They are numbered 1 to 4 in the counter-clockwise direction starting from the upper right quadrant. The quadrant numbers are denoted by Roman numerals.
Line segment
A line segment is a part of a line that has two distinct and finite end points. For example, sides of a triangle or a square or any other geometric figure that has distinct end points.
Variable
A variable is a placeholder for a number. It is denoted by an alphabet. For example, in 5x - 7, x is a variable. The value given to x will determine the value of 5x - 7.
Constant
A constant is a static number in an equation. For example, in the equation y = x - 7, 7 is a constant. Its values will not change in the equation.
Sometimes a constant may be denoted by an alphabet in an equation. A question that has an alphabet as a constant will specifically call out the constant. For example, in the equation y = x - a, a is a constant.
Coefficient
A coefficient is a constant number multiplied by a variable. For example, in the equation 2y = 5x - 7, 2 is the coefficient of the variable y and 5 is the coefficient of the variable x.
Every variable has a coefficient. If a number is not given in front of the variable, then the value of the variable is 1. For example, in the equation 2y = x - 7, the coefficient of the variable x is 1.
Term
A term is referred to a number, a variable, several variables multiplied together, or a number and several variables multiplied together. For example, in the equation 2xy + x + 7 = y - 1, the terms on the left-side of the equation are 2xy, x, and 7 and the terms on the right-side of the equation are y and 1.
Expression
The terms on either side of an equation are collectively known as an expression. For example, in the equation 2x + 7 = x - 1, the two expressions are 2x + 7 and x - 1. An expression can be comprised of multiple terms and can contain plus, minus, multiplication, or division operators.
The distinction between an expression and an equation is important to remember. An equation contains an equal sign that equates two equal expressions, one on the left-side of the equal sign and one on the right-side of the equal sign.
Tangent
When two geometric figure in the xy-plane touch at one point, they are tangent to each other. For example, two circles are tangent to each other when they touch at one point, a line is tangent to a circle when it touches the circle at one point, a line is tangent to a parabola when it touches the parabola at one point, and so on.
Words/Phrases
Linear relationship between two variables
This implies that the two variables are the coordinates of points on a line.
Zeros/Roots/Solutions/x-intercepts of the polynomial/quadratic function
The above terms refer to the same thing in a question on polynomial/quadratic equation. They refer to the points on the x-axis where the graph of a function intersects or touches the x-axis.
x-coordinate of the x-intercept
y is 0 at the x-intercept. Hence, the coordinates of the x-intercept are (x, 0). x is the x-coordinate of the x-intercept.
y-coordinate of the y-intercept
x is 0 at the y-intercept. Hence, the coordinates of the y-intercept are (0, y). y is the y-coordinate of the y-intercept.
True for all values of x
This implies that the equation or the system of equations in the question has infinitely many solutions.
Minimum/Maximum appears as constants or coefficients
This phrase refers to the vertex of a parabola in a quadratic function. When the parabola opens downwards, it is referred to as the maximum. When the parabola opens upwards, it is referred to as the minimum.
Half/Double/Increase or decrease by x% over a certain period
These terms refer to exponential growth or decay. Increase is growth and decrease is decay.
Plausible average increase/decrease
This refers to the value of the constant associated with the unknown number in the given linear equation.
Algebra Flash Cards
Lines and Slope


Solutions of linear system of equations

Quadratic equation

Discriminant in a quadratic equation

Equations of a parabola

Factor theorem and Remainder theorem

Percent

Exponential growth and decay

Compound interest rate

Absolute value linear inequalities

Geometry, Trigonometry, and Complex Numbers Flash Cards
Radians and degrees

Congruent angles

Supplementary angles

Area of a circle and sector of a circle

Circumference of a circle and length of an arc

Equation of a circle

Area of a triangle

Special right triangles

Right triangle and Pythagorean theorem

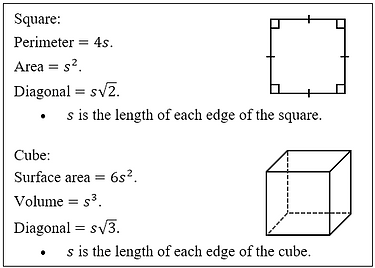
Square and cube
Rectangle and right rectangular prism

Area of a trapezoid

Area of a parallelogram

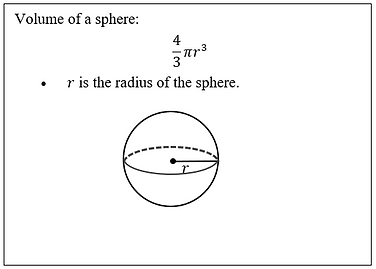
Volume of a sphere
Volume of a cone

Volume of a right rectangular prism

Volume of a right cylinder

Trigonometric functions

